Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium
Topic Description
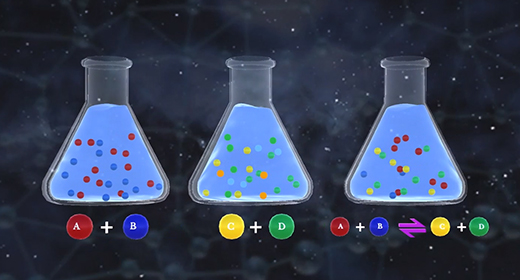
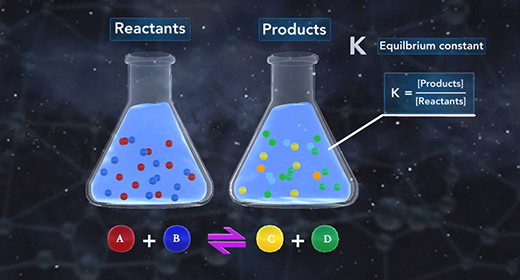
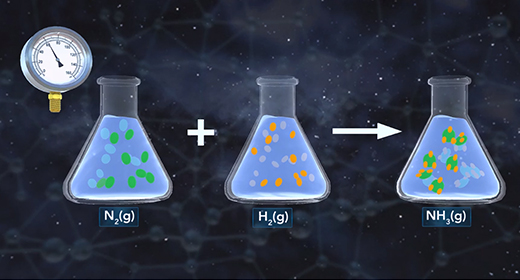
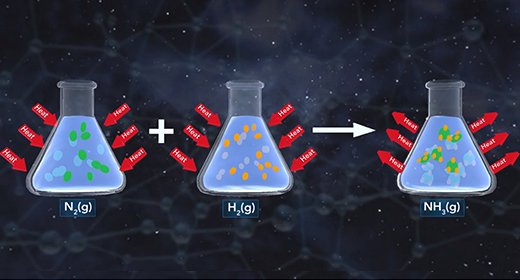
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to understand how changes in temperature, pressure, and concentration affect equilibrium and understand the relationship between the rate of reaction and equilibrium. Equilibrium is the state of a reaction in which products and reactants form at the same rate. Rate of forwarding reaction = rate of the reverse reaction. Accordingly, there is no net gain in the mass of the product or reactant. At equilibrium, the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants remains unchanged, and this ratio is known as the equilibrium constant.

The topic "Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.