Corporate Headquarters
475 Metro place South, Suite 120, Dublin, OH 43017, USA,
Direct: +1 614-707-5225
Global Technology Center
SKCL Infinite Towers, A21 & A22, Thiru-vi-ka Ind. Estate, Guindy, Chennai-600032, India,
Direct: +91 (44)-2250-1363
Virtual Reality
in Healthcare
Virtual Reality (VR) is revolutionizing healthcare by improving advanced medical training, personalizing patient care, expanding therapy options, and improving outcomes.
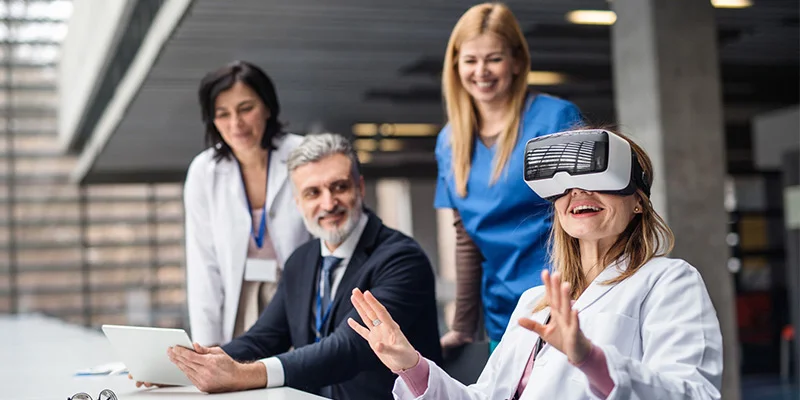

Why Use Virtual Reality (VR) in Healthcare
Enhanced Medical Training
VR provides realistic simulations and interactive scenarios for medical training, enabling healthcare professionals to practice procedures in a safe and controlled environment. This leads to better skill acquisition and retention, ultimately improving patient care.

Improved Patient Education
Patients can better understand their medical conditions, treatment options, and procedures through immersive VR experiences. This enhanced understanding promotes patient engagement, treatment plan adherence, and overall healthcare service satisfaction.
Pain Distraction and Management
VR offers immersive experiences that can distract patients from pain and discomfort during medical procedures or treatments. By providing engaging content and interactive environments, VR can help reduce anxiety and improve the patient experience.

Medical Visualization and Education
VR allows healthcare professionals to visualize complex medical data, such as imaging scans or patient anatomy, in three-dimensional space. This improves understanding, communication, and decision-making in medical education and clinical practice.
Use Cases
Explore Examples of VR Healthcare Solutions
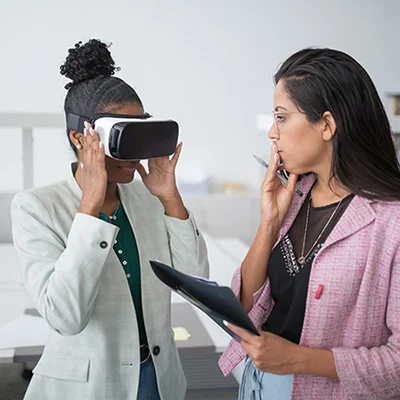

Medical Training
Virtual Reality (VR) software that focuses on practical medical training helps medical school graduates and healthcare professionals acquire hands-on skills in low-risk conditions. This type of healthcare VR allows the simulation of complex, dangerous, or expensive scenarios to recreate in real life. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality for medical training work by enabling users to enter a simulated environment in which they become part of a training scenario that expects them to complete predetermined steps, for instance, performing a medical procedure or handling medical equipment. A separate analytical module continuously records the actions taken and assesses a medical professional’s performance based on set criteria.
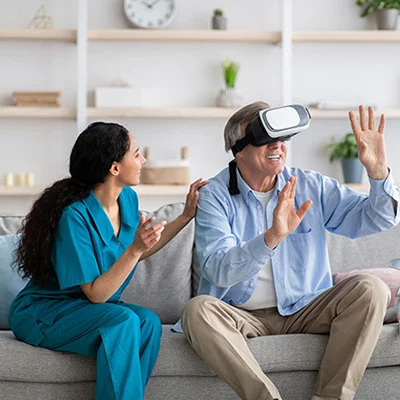

Stroke Rehabilitation
To effectively recover after a stroke, patients re-learn to perform their typical daily actions in the virtual environment. Patients can access a rich database of exercises that help them restore motor skills or improve spatial orientation abilities without posing any risks of damage to themselves, others, or the objects they manipulate. The rehabilitation can be remote, thus significantly minimizing treatment and transportation costs. Virtual Reality technology, such as Virtual Reality for stroke rehabilitation, allows post-stroke patients to perform repetitive exercises in the VR world; the integrated machine-learning algorithms continuously monitor their performance and automatically adjust the difficulty to ensure progress.
Surgery
By allowing surgeons to perform different types of mock surgeries in the virtual space, Virtual Reality (VR) helps eliminate practical skill deficiency faster. Surgeons can become skilled professionals without using expensive onetime use mannequins for training. Virtual Reality (VR) for surgery allows a surgeon to perform virtual surgery in a virtual operating room. From start to finish, software guides the user through the necessary steps, letting them remember the correct sequence of actions. The VR app can also be used to explain the surgery process to patients.
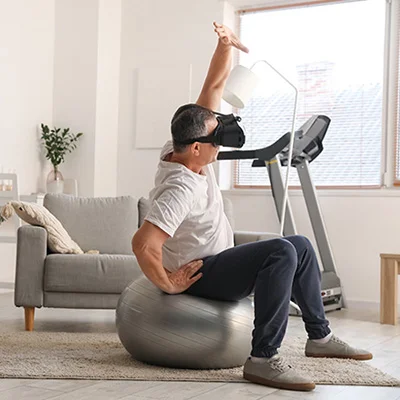

Pain Management
Virtual Reality (VR) pain management apps help lower pain or extreme discomfort by effectively diverting a patient’s attention. This type of VR helps minimize the use of potentially harmful painkillers and reduce healthcare costs. Virtual Reality (VR) for pain management works by immersing a patient in a VR simulation. After being immersed in the VR simulation, the patient can either become a part of an interactive gamified experience or be transferred to a highly realistic environment with a soothing atmosphere that, together with audio stimulation, helps put their mind at ease..
Most Popular Packages for Healthcare
XR Guru
CNA and Medical Assistant Skills
Designed to train healthcare assistant essential skills with interactive, hands-on practice
For 1 user $799.99 - 12 months
View DetailsGleechi Technology AB
Dental Assistant
Explore 27 dental procedures, freely practicing and developing hands-on skills

For 1 user $1,200.00 - 12 months
View DetailsXennial Digital
VR Anesthesia and Intubation Simulation Labs
Master Anesthesia Procedures and build Confidence in a Risk-free Virtual Reality Operating Room

For 1 user $15,000.00 - 12 months
View DetailsXR Guru
Comprehensive Human Anatomy
Visualize the Complexities of Human Anatomy in Virtual Reality

For 5 users $495.00 - 12 months
View DetailsFrequently Asked Questions
How Virtual Reality improves healthcare?
Virtual Reality is much more than just a new form of entertainment; it is increasingly used in various medical applications, from treatments to training. Here are a few of them. Pain Management: There is good scientific evidence that Virtual Reality (VR) can help relieve pain. The brain parts linked to pain are less active when a patient is immersed in virtual reality. Sometimes, it can even help people tolerate medical procedures that are usually very painful. Physical Therapy: It’s more fun doing exercises in Virtual Reality than in a gym, so people are more motivated to exercise. In addition, studying how people perceive and interact with VR systems helps design better rehabilitation applications. Fears and Phobias: Virtual Reality effectively treats people with fears and phobias, for it can be adjusted precisely for the needs of each patient. VR is used to treat phobias such as fear of heights and fear of spiders, as well as to help people recover from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Cognitive Rehabilitation: Patients with brain injury from trauma or illness, such as stroke, often struggle with everyday tasks. Recreating these tasks within virtual environments and allowing patients to practice them at increasing levels of complexity can speed up recovery and help patients regain a higher level of cognitive function. Training Healthcare Professionals: Virtual Reality is used to learn anatomy, practice operations, and teach infection control. Being immersed in a realistic simulation of a procedure and practicing the steps and techniques is far better training than watching a video or even watching an expert. With controllable, repeatable scenarios and instant feedback, VR is a powerful new teaching tool that reaches beyond the classroom.
What are the benefits of VR in healthcare?
Here are some benefits that companies in the healthcare field may experience by implementing VR technology. VR enhances medical training by giving medical students an immersive first-hand view of any medical procedure. With a VR headset and a controller, students can step into an immersive virtual representation of actual surgical procedures. VR significantly improves the quality of medical training while serving as a cost-effective method of educating a new generation of healthcare professionals. VR technology reduces the risk for patients and healthcare professionals. For example, VR helps surgeons to work out the surgery beforehand while playing out various scenarios. They can optimize the sequence and prepare a course of action even for extreme circumstances. In this way, the operation will become more precise and controlled. VR provides better pain management. VR effectively diverts a patient's attention by immersing them in a VR simulation where they can either become a part of an interactive experience or be transferred to a highly realistic environment with a soothing atmosphere. VR enhances physical rehabilitation. VR technology allows patients with different neurological disorders to execute actions they cannot perform in real life due to their disabilities. VR improves patient-physician consultations. Physician consultation is only sometimes available in remote locations. Adopting VR services allows doctors to provide consistent patient-physician communication. Additionally, it offers essential services like pulse examination and understanding emotional responses.
What are the dangers of Virtual Reality in healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) provides several benefits to the healthcare industry for both healthcare professionals and patients. Potential applications of VR in healthcare include training clinicians; enhancing patient care; helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, and improving patient education through simulation exercises. However, VR is not for everyone. Most people can use VR without problems. A few get “cyber sickness,” nausea that’s similar to that of motion sickness. It goes away when you take off the headset. Better, faster hardware and software mean this issue is happening less often. VR also has its limitations. For example, it’s not recommended to use VR for practicing procedures that rely on thorough palpation or involve surgical drilling since highly-detailed surfaces and vibration feedback are hard to simulate. However, even with its potential issues and limitations, it provides several benefits, including thinking about the role of the mind and its connection to the body. VR requires healthcare professionals to understand the patient in a different, more holistic way - resulting in a more humanizing way of thinking about people and how to best care for them.
How are VR applications helpful in safety and training in healthcare sectors?
Virtual Reality (VR) training is customizable, portable, and accessible, making it an excellent fit for the healthcare industry. VR is currently being used in healthcare training by companies like Seattle Children’s Hospital, the Mayo Clinic, Bayer , and Johns Hopkins in various ways, including patient education, 3D surgical simulations, mental health treatments, therapy, pain management, and rehabilitation. Organizations that have embraced VR for learning have found it to be an interactive and “hands-on” way to deliver important – sometimes critical – content memorably and effectively.
How Virtual Reality Is used in the healthcare industry?
VR is on the upswing - because recent advancements and government initiatives have given the technology some momentum. The Virtual Reality healthcare market is booming, and as a result, the applications of VR in healthcare are numerous. VR makes it easier for many medical professionals to conduct surgeries, educate patients, facilitate rehab and therapy, and take care of back-office work. Today, VR is used to teach communication skills to people with autism, detect vision impairment, access medical records, prepare for surgery, and improve physical therapy and rehabilitation. As impressive as it may seem now, VR is a rapidly advancing technology and there are almost certainly more dazzling developments ahead.
How Virtual Reality is changing the healthcare industry?
Virtual Reality (VR) is on the rise, and there are endless possibilities for its implementation; one of the most exciting is healthcare use. The implementation of VR technology in clinics and other healthcare settings has been up and coming in the past few years. Its applications range from cognitive and physical rehabilitation to pain relief and spreading disease awareness, with more uses being developed daily. There are countless examples of applications within the Healthcare market. For example, VR technology is used to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of medical training; enhance health communication and disease awareness; relieve anxiety, stress, and pain; help treat phobias; and increase healthcare accessibility.
How VR is set to change the healthcare industry?
Virtual Reality is becoming a part of our daily lives at an astonishing pace. While the primary use was for gaming purposes, VR is increasingly used in many other sectors and industries. You can find it in education, engineering, sports, advertising, entertainment, healthcare, and many other fields. The importance of VR in healthcare has reached new peaks, and its use is present in many medical areas. The ultimate goal of healthcare is to make people feel better and healthier. To this end, VR is used by doctors and healthcare workers for educational purposes and by patients as a therapy to treat symptoms. One of the primary uses of VR in healthcare is in planning surgery. Surgeons use this tool to prepare for any procedures and go through all the steps without any pressure. By being able to visualize the entire process, the success of the surgery is significantly increased. Another fantastic example of Virtual Reality transforming healthcare is its use in educating and training medical professionals. VR allows healthcare professionals to learn new skills and refresh existing ones in a safe environment. Plus, it allows this without causing any danger to the patients. This kind of learning offers unique possibilities, and the quality of future doctors is heightened. Diagnostics is another area where VR is already making its presence felt. Virtual Reality can aid doctors in making more accurate diagnoses for various medical cases. It can even eliminate the need to opt for invasive techniques to identify the problem. Other ways VR is transforming healthcare include enhancing patient care, helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, and improving patient education through simulation exercises.
What is Virtual Reality (VR) in healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) is a technology that allows users to experience virtual spaces. The main advantages are that the user is no longer confined to one location and can be in any environment, allowing for a more immersive experience. VR offers several benefits to the healthcare industry. One of the most important advantages is that it reduces pain associated with physical therapy; another key advantage is its ability to allow a user to interact with an avatar while performing exercises in a virtual environment, which improves muscle control. Another vital use of VR in healthcare is in planning surgery. Surgeons use VR to prepare for procedures and go through all the steps. By being able to visualize the entire process, the success of the surgery is significantly increased. Today, medical professionals use VR-based simulation technologies to practice real-life, complex procedures using combinations of 3D interaction and 360-degree videos. Medical professionals can practice on virtual patients or cadavers as if they are real and perform everything from a simple blood test to complex heart surgery and even an autopsy. Also, VR can be used to train healthcare professionals on how to better interact with their patients and create a positive therapeutic environment for them during treatment sessions. Other applications include dentistry, PTSD, autism treatment, and treatment for the disabled.
How big is the Virtual Reality in healthcare Industry?
The COVID-19 pandemic greatly hastened the adoption of virtual technology in the healthcare industry. Virtual healthcare services became a necessity for millions of people as efforts to slow the spread of coronavirus disease sharply limited face-to-face visits. The global Virtual Reality (VR) in healthcare market size was valued at $459.0 milion in 2021. The market is projected to grow from $628.0 million in 2022 to $6.20 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 38.7%
What are the key Virtual Reality in healthcare industry drivers?
According to Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research, healthcare is among the top 3 industries that will remain leading adopters of VR technology up to 2025. The COVID-19 pandemic greatly hastened the adoption of virtual technology in the healthcare industry. Virtual healthcare services became necessary for millions of people as efforts to slow the spread of coronavirus disease sharply limited face-to-face visits. Other key drivers of the growing VR adoption in healthcare are the extreme demand for quality healthcare services, the need to reduce healthcare costs, and the increased role of connected devices in the healthcare sector.
How is VR helpful in training healthcare technicians?
VR in healthcare is still relatively new, but it has already shown promise as a tool for training technicians. Some experts believe this form of training will become more critical than traditional hands-on training methods such as lectures and case studies. For instance, the Nicklaus Children’s Hospital in Miami uses VR training scenarios to teach procedures like Foley catheter insertion, starting an IV, the Heimlich maneuver, wound care, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and nasal-gastric tube insertion. The hospital reports that the retention level remained at 80% one whole year after training, compared to a traditional training methods retention level of 20% after only a week. These results prove that virtual reality is poised to revolutionize the healthcare training industry, enabling critical, time-sensitive, and job-specific training. Enabling exploratory learning in a risk-free environment is ideal for formative learning and training.
Why should I opt VR for healthcare?
Today, more and more healthcare businesses are investing in VR technology to receive the benefits it can bring. Implementing VR-based tools and devices can help healthcare organizations improve staff productivity and patient satisfaction. VR is making great strides in the healthcare industry by providing engaging education and training for medical professionals and students, innovatively treating patients with neuropsychological issues, acting as a potential tool for pain relief, providing therapy for people with chronic illnesses or disabilities, and more. According to Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research, healthcare is among the top 3 industries that will remain leading adopters of VR technology up to 2025.
How will Virtual Reality impact healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) is redefining what is possible in the healthcare industry. Today, Virtual Reality is used in the healthcare industry for everything from surgical preparation to patient education, rehabilitation, and therapy. Patients are already benefiting from advanced and more precise surgeries, simulations for mental illness treatments, and many other improvements thanks to VR solutions. VR helps make healthcare professionals' work more effective and patients' lives easier.
Why choose VR for healthcare?
Today, more and more healthcare businesses are willing to invest in VR technology to reap its benefits. Implementing VR-based tools and devices can help healthcare organizations improve staff productivity and patient satisfaction. VR solutions are providing new options to achieve desired outcomes in the healthcare domain. Benefits provided by VR include providing engaging education and training for medical professionals and students, reducing the risk to patients and healthcare professionals, offering better pain management, enhancing physical rehabilitation, treating autism, fighting memory loss, treating people with fears and phobias, and improving patient-physician consultation.
Is Virtual Reality the future of the healthcare industry?
Using VR simulation is not new to healthcare; over the years, companies have developed VR-based simulation technologies to help physicians and medical students practice real-life, complex procedures using combinations of 3D interaction and 360-degree videos. Students can practice on virtual patients or cadavers as if they are real and perform everything from a simple blood test to complex heart surgery and even an autopsy. VR offers tools for treating mental illness, improving pain management, helping in diagnoses, enhancing patient care, helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, improving patient education through simulation exercises, and more. With all these applications already existing, combined with future predictions for growth, it appears VR in healthcare is here to stay!
How is VR used in surgery?
One of the primary uses of VR in healthcare is planning surgery. Surgeons use this tool to prepare for any procedures and go through all the steps in a safe environment without any pressure. By being able to visualize the entire process, the success of the surgery is significantly increased. Another advantage of employing VR in preoperative planning is creating a surgical rehearsal environment where patients and surgeons can go through an upcoming surgery in VR for a better understanding of a scenario. Today, it is not uncommon to find robots performing complex surgeries with a surgeon's control; or tele-surgeries performed by a doctor from a different location altogether. Robotic surgery is becoming popular in healthcare because it minimizes the time, complexity, and potential complications arising from certain types of tricky cases. Surgical robots are solutions built at the intersection of robotics and virtual reality. The robot’s purpose is to maximize visualization and precision in minimally invasive, robotic-assisted surgeries. VR allows the surgeon to be fully immersed inside a patient’s body and has 360-degree access. The robot’s arms are designed to replicate a surgeon’s body movement, from shoulders to wrists.
When did VR start being used in healthcare?
Virtual Reality in healthcare started in the 1990s. Back then, research teams from the University of North Carolina and the US Department of Defense began equipping surgeons with the first VR headsets and tried “real” procedures with computer-generated images. After studies like this showed positive results, it became a growing market for VR development and optimism around surgical simulation. The COVID-19 pandemic greatly hastened the adoption of virtual technology in the healthcare industry. Virtual healthcare services became necessary for millions of people as efforts to slow the spread of coronavirus disease sharply limited face-to-face visits. Today, VR technology can improve many people's lives, from those looking to stay fit to patients with traumas and phobias.
What is Virtual Reality in healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) is a technology that allows users to experience virtual spaces. The main advantages are that the user is no longer confined to one location and can be in any environment, allowing for a more immersive experience. Recently, VR in healthcare has made significant strides. Although the technology is relatively new, there are several benefits to using it today. One significant advantage is that it reduces pain associated with physical therapy; another key advantage is its ability to allow a user to interact with an avatar while performing exercises in a virtual environment, which improves muscle control. Applications of VR in healthcare include training clinicians; enhancing patient care; helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, and improving patient education through simulation exercises.
What is the future of Virtual Reality in healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) has a bright future in healthcare. Today, Virtual Reality (VR) benefits the healthcare industry for both healthcare professionals and patients. Current applications of VR in healthcare include training clinicians; enhancing patient care; helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, and improving patient education through simulation exercises. Given all the benefits and applications VR offers, we can safely conclude that Virtual Reality has a bright future in healthcare. Some future projects may include environments for designing new medicine or even experimental procedures that otherwise could not be taken due to safety issues. Virtual Reality is transforming healthcare more and more, and with the speed at which progress is happening, the impact made by VR on healthcare reaches new heights every year!
What are VR applications in healthcare?
The Virtual Reality (VR) healthcare market is booming. As a result, the applications of VR in healthcare are numerous. For example, VR is used for educating and training medical students, doctors/surgeons, nurses, and other medical professionals; preoperative planning; chronic pain treatment; treatment of mental disorders and phobias, and more. VR makes it easier for many medical professionals to conduct surgeries, educate patients, facilitate rehab and therapy, and take care of back-office work. What is Virtual Reality in healthcare market size?
The COVID-19 pandemic greatly hastened the adoption of virtual technology in the healthcare industry. Virtual healthcare services became a necessity for millions of people as efforts to slow the spread of coronavirus disease sharply limited face-to-face visits. The global Virtual Reality (VR) in healthcare market size was valued at $459.0 milion in 2021. The market is projected to grow from $628.0 million in 2022 to $6.20 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 38.7%
How is VR growing in healthcare?
One way VR is growing in healthcare is by increasing healthcare accessibility. VR technology in healthcare increases accessibility to healthcare with only a VR headset and the appropriate VR application for treatment. The ease of accessibility can shift care delivery from a medical facility to the safety and security of one’s home. With the possibility of medical care in a familiar environment, patients' quality of life can also be increased. As VR treatment can lead to more efficiency and effectiveness for medical practitioners, the number of people that can be treated can increase, thus expanding the reach and availability of medical care for all. VR is also growing in healthcare by providing effective training for healthcare professionals, treating people with fears and phobias, assisting with pain management, and enhancing physical therapy and cognitive rehabilitation.
Why Virtual Reality is the future of healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) is here to stay. However, it is currently limited by the technology needed to make it work properly. For example, graphics and graphics quality need to be very high; in addition, viewers must be able to see the object being viewed and interact with it - this can be achieved using VR headsets to view a Virtual Reality experience. But this adds more cost and complexity. Companies are working on new ways of creating VR experiences that do not require special glasses or expensive equipment. The critical differentiator between Virtual Reality and other forms of advanced training is that VR has no limit on what you can do with it. Some experts believe that this form of training will become more critical because there will be fewer limits on how you train — potentially allowing for more realistic learning outcomes as well as better client care/career development outcomes for professionals who are already trained in healthcare settings such as doctors, nurses, and pharmacists. While Virtual Reality (VR) can be used in different ways, its immersive nature makes it stand out from other forms of technology.
Do doctors in the healthcare industry use Virtual Reality?
Doctors use VR in healthcare in planning surgery. Surgeons use this tool to prepare for any procedures and go through all the steps without any pressure. By being able to visualize the entire process, the success of the surgery is significantly increased. Diagnostics is another area where doctors are using VR. Virtual Reality can aid doctors in making more accurate diagnoses for various medical cases. It can even eliminate the need to opt for invasive techniques to identify the problem. In addition, doctors are using VR to improve patient-physician consultation. For example, physician consultation is not always available in remote locations. In such cases, adopting Virtual Reality (VR) services allows doctors to provide consistent patient-physician communication. Additionally, it offers essential services like pulse examination and understanding emotional responses.
What are the pros and cons of Virtual Reality in healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) provides several benefits to the healthcare industry for both healthcare professionals and patients. Potential applications of VR in healthcare include training clinicians; enhancing patient care; helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, and improving patient education through simulation exercises. However, VR is not for everyone. Most people can use VR without problems. A few get “cyber sickness,” nausea that’s similar to that of motion sickness. It goes away when you take off the headset. Better, faster hardware and software mean this issue is happening less often. VR also has its limitations. For example, it’s not recommended to use VR for practicing procedures that rely on thorough palpation or involve surgical drilling since highly-detailed surfaces and vibration feedback are hard to simulate. However, even with its potential issues and limitations, VR provides several benefits, including thinking about the role of the mind and its connection to the body. VR helps healthcare professionals to understand the patient in a different, more holistic way - resulting in a more humanizing way of thinking about people and how to best care for them.
How can VR be used in medical education?
Virtual Reality makes for more effective theoretical learning for medical students and new healthcare professionals. With VR, learners can inspect 3D medical models in detail, which can’t be reproduced in physical models, or learn to communicate with virtual patients whose attitudes and behavior can be easily altered for different learning purposes. VR technology provides medical students with an immersive first-hand view of any medical procedure, even if they are not in the operating room. With a VR headset and a controller, students can step into an immersive virtual representation of actual surgical procedures. Virtual Reality (VR) software that focuses on practical medical training helps medical school graduates and healthcare professionals acquire hands-on skills in low-risk conditions. This type of healthcare VR allows the simulation of scenarios that are difficult, dangerous, or expensive to recreate in real life. Primary use cases for VR medical education include anatomy and medical social skills learning.
Is VR the future of the healthcare industry?
Using VR simulation is not new to healthcare; over the years, companies have developed VR-based simulation technologies to help physicians and medical students practice real-life, complex procedures using combinations of 3D interaction and 360-degree videos. Students can practice on virtual patients or cadavers as if they are real and perform everything from a simple blood test to complex heart surgery and even an autopsy. VR offers tools for treating mental illness, improving pain management, helping in diagnoses, enhancing patient care, helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, improving patient education through simulation exercises, and more. With all these applications already existing, combined with future predictions for growth, it appears VR in healthcare is here to stay!
What is Virtual Reality (VR) in healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) is an umbrella term for any technology that alters reality by adding digital elements to the physical or real-world environment to any extent and includes Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). Augmented Reality (AR) is an enhanced version of the real physical world that is achieved through digital visual elements, sound, or other sensory stimuli and delivered via technology. Virtual Reality (VR) is a technology that allows users to experience virtual spaces. The main advantages are that the user is no longer confined to one location and can be in any environment, allowing for a more immersive experience. Recently, VR in healthcare has made significant strides. Although the technology is relatively new, there are several benefits to using it today. One significant advantage is that it reduces pain associated with physical therapy; another key advantage is its ability to allow a user to interact with an avatar while performing exercises in a virtual environment, which improves muscle control. Potential applications of AR and VR in healthcare include training clinicians; enhancing patient care; helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, and improving patient education through simulation exercises.
What are the dangers of Virtual Reality in healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) provides several benefits to the healthcare industry for both healthcare professionals and patients. Potential applications of VR in healthcare include training clinicians; enhancing patient care; helping patients overcome the fear of undergoing physical therapy, and improving patient education through simulation exercises. However, VR is not for everyone. Most people can use VR without problems. A few get “cyber sickness,” nausea that’s similar to that of motion sickness. It goes away when you take off the headset. Better, faster hardware and software mean this issue is happening less often. In addition, VR has its limitations. For example, it’s not recommended to use VR for practicing procedures that rely on thorough palpation or involve surgical drilling since highly-detailed surfaces and vibration feedback are hard to simulate. However, even with its potential issues and limitations, VR provides several benefits, including thinking about the role of the mind and its connection to the body. VR helps healthcare professionals to understand the patient in a different, more holistic way - resulting in a more humanizing way of thinking about people and how to best care for them.
What are the benefits of VR in healthcare?
Here are some benefits that companies in the healthcare field may experience by implementing VR technology. VR enhances medical training by giving medical students an immersive first-hand view of any medical procedure. With a VR headset and a controller, students can step into an immersive virtual representation of actual surgical procedures. VR significantly improves the quality of medical training while serving as a cost-effective method of educating a new generation of healthcare professionals. VR technology reduces the risk for patients and healthcare professionals. For example, VR helps surgeons to work out the surgery beforehand while playing out various scenarios. They can optimize the sequence and prepare a course of action even for extreme circumstances. In this way, the operation will become more precise and controlled. VR provides better pain management by effectively diverting a patient's attention by immersing them in a VR simulation where they can either become a part of an interactive experience or be transferred to a highly realistic environment with a soothing atmosphere. VR enhances physical rehabilitation as it allows patients with different neurological disorders to execute actions they cannot perform in real life due to their disabilities. VR improves patient-physician consultations. Physician consultation is only sometimes available in remote locations. Adopting VR services allows doctors to provide consistent patient-physician communication. Additionally, it offers essential services like pulse examination and understanding emotional responses.
How is VR transforming healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) is redefining what is possible in the healthcare industry. Today, Virtual Reality is used in the healthcare industry for everything from surgical preparation to patient education, rehabilitation, and therapy. Patients are already benefiting from advanced and more precise surgeries, simulations for mental illness treatments, and many other improvements thanks to VR solutions. VR helps make healthcare professionals' work more effective and patients' lives easier.
How is Virtual Reality changing the healthcare industry?
Virtual Reality (VR) is on the rise, and there are endless possibilities for its implementation; one of the most exciting is healthcare use. The implementation of VR technology in clinics and other healthcare settings has been up and coming in the past few years. Its applications range from cognitive and physical rehabilitation to pain relief and spreading disease awareness, with more uses being developed daily. There are countless examples of applications within the Healthcare market. For example, VR technology is used to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of medical training; enhance health communication and disease awareness; relieve anxiety, stress, and pain; help treat phobias; and increase healthcare accessibility.
How is VR being used in the healthcare industry?
VR is on the upswing - because recent advancements and government initiatives have given the technology some momentum. The Virtual Reality healthcare market is booming, and as a result, the applications of VR in healthcare are numerous. VR makes it easier for many medical professionals to conduct surgeries, educate patients, facilitate rehab and therapy, and take care of back-office work. Today, VR is used to teach communication skills to people with autism, detect vision impairment, access medical records, prepare for surgery, and improve physical therapy and rehabilitation. As impressive as it may seem now, VR is a rapidly advancing technology and there are almost certainly more dazzling developments ahead.
How do VR applications help in training in the healthcare sector?
Virtual Reality (VR) training is customizable, portable, and accessible, making it an excellent fit for the healthcare industry. VR is currently being used in healthcare training by companies like Seattle Children’s Hospital, the Mayo Clinic, Bayer , and Johns Hopkins in various ways, including patient education, 3D surgical simulations, mental health treatments, therapy, pain management, and rehabilitation. Organizations that have embraced VR for learning have found it to be an interactive and “hands-on” way to deliver important – sometimes critical – content memorably and effectively.
What is the role of Virtual Reality in healthcare education?
Virtual Reality makes for more effective theoretical learning for medical students and new healthcare professionals. With VR, learners can inspect 3D medical models in detail, which can’t be reproduced in physical models, or learn to communicate with virtual patients whose attitudes and behavior can be easily altered for different learning purposes. VR technology provides medical students with an immersive first-hand view of any medical procedure, even if they are not in the operating room. With a VR headset and a controller, students can step into an immersive virtual representation of actual surgical procedures. Virtual Reality (VR) software that focuses on practical medical training helps medical school graduates and healthcare professionals acquire hands-on skills in low-risk conditions. This type of healthcare VR allows the simulation of scenarios that are difficult, dangerous, or expensive to recreate in real life. Primary use cases for VR medical education include anatomy and medical social skills learning.
Why integrate VR into healthcare?
Today, more and more healthcare businesses are investing in VR technology to receive the benefits it can bring. Implementing VR-based tools and devices can help healthcare organizations improve staff productivity and patient satisfaction. VR is making great strides in the healthcare industry by providing engaging education and training for medical professionals and students, innovatively treating patients with neuropsychological issues, acting as a potential tool for pain relief, providing therapy for people with chronic illnesses or disabilities, and more. Virtual Reality is transforming healthcare more and more, and with the speed at which progress is happening, the impact of VR on healthcare reaches new heights every year!



